Płyta Nazca
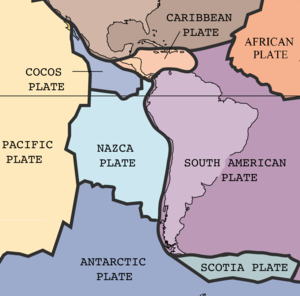
Płyta Nazca – płyta tektoniczna, która swoją powierzchnią obejmuje południowo-wschodnią część Oceanu Spokojnego, jest więc typową płytą oceaniczną.
Na zachodzie, poprzez Grzbiet Wschodniopacyficzny graniczy z płytą pacyficzną, na północy z płytą kokosową, na wschodzie, poprzez Rów Atakamski z płytą południowoamerykańską, a na południu, poprzez Grzbiet Chilijski z płytą antarktyczną.
W południowej części płyty Nazca znajdują się Grzbiet Juan Fernandez i Grzbiet Nazca, a w północnej Grzbiet Galapagos.
Według tektoniki płyt płyta Nazca wsuwa się pod płytę południowoamerykańską, powodując powolne wypiętrzanie się Andów.
Media użyte na tej stronie
The key principle of plate tectonics is that the lithosphere exists as separate and distinct tectonic plates, which float on the fluid-like (visco-elastic solid) asthenosphere. The relative fluidity of the asthenosphere allows the tectonic plates to undergo motion in different directions. This map shows 15 of the largest plates. Note that the Indo-Australian Plate may be breaking apart into the Indian and Australian plates, which are shown separately on this map.
The key principle of plate tectonics is that the lithosphere exists as separate and distinct tectonic plates, which float on the fluid-like (visco-elastic solid) asthenosphere. The relative fluidity of the asthenosphere allows the tectonic plates to undergo motion in different directions. This map shows 15 of the largest plates. Note that the Indo-Australian Plate may be breaking apart into the Indian and Australian plates, which are shown separately on this map.