Zimowe Igrzyska Olimpijskie 2002
| Ten artykuł od 2021-03 wymaga zweryfikowania podanych informacji. |
 | |
| Stolica igrzysk | |
|---|---|
| Liczba ekip | 77 |
| Liczba sportowców | 2399 |
| Liczba konkurencji | 78 w 9 dyscyplinach |
| Otwarcie | |
| Oficjalne otwarcie | |
| Zamknięcie | |
| Przysięga olimpijska | |
| Znicz olimpijski | Hokejowa reprezentacja USA, która w 1980 r. dokonała Cudu na lodzie, na czele z Mikiem Eruzionem |
| Stadion | |
XIX Zimowe Igrzyska Olimpijskie odbyły się w amerykańskiej miejscowości Salt Lake City od 8 do 24 lutego 2002. Startowało 2527 zawodników z 78 krajów. Na zimowych igrzyskach zadebiutowali przedstawiciele 5 państw: Kamerunu, Hongkongu, Nepalu, Tadżykistanu i Tajlandii. Igrzyska otworzył prezydent USA George W. Bush.
Wybór gospodarza
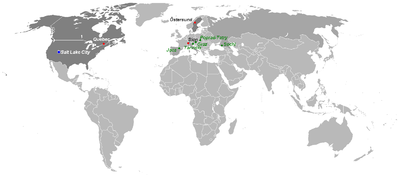
Do organizacji zimowych igrzysk olimpijskich w 2002 roku kandydowało cztery miasta: Québec, Sion, Östersund oraz Salt Lake City. W czerwcu 1995 roku w Budapeszcie, Międzynarodowy Komitet Olimpijski wybrał z tego grona miasto organizatora igrzysk.
| Wyniki głosowania na gospodarza Zimowych Igrzysk Olimpijskich 2002 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Miasto | Państwo | Runda 1 | ||||
| Salt Lake City | 54 | |||||
| Östersund | 14 | |||||
| Sion | 14 | |||||
| Québec | 7 | |||||
Ostatecznie gospodarza wyłoniono 16 czerwca 1995 roku, podczas 104. sesji Międzynarodowego Komitetu Olimpijskiego w Budapeszcie. Już w pierwszej turze głosowania, z liczbą 54 głosów, zwyciężyło amerykańskie Salt Lake City.
Dyscypliny olimpijskie
- biathlon (debiut biegu pościgowego)
- bobsleje (debiut kobiecych dwójek)
- curling
- hokej na lodzie
- łyżwiarstwo
- łyżwiarstwo szybkie
- łyżwiarstwo szybkie
- short track (debiut 1500 m)
- łyżwiarstwo figurowe
- łyżwiarstwo synchroniczne (sport pokazowy)
- łyżwiarstwo szybkie
- narciarstwo
- narciarstwo klasyczne
- biegi narciarskie (debiut sprintu, zmiana techniki na klasyczną w biegu na 30 km kobiet, zmiana na styl dowolny w biegu na 15 km kobiet, 15 km klas. zastępuje 10 km dow. u mężczyzn, 10 km klas. zastępuje 5 km klas. u kobiet)
- skoki narciarskie
- kombinacja norweska (debiut sprintu)
- narciarstwo alpejskie
- narciarstwo dowolne
- snowboarding (slalom równoległy zastępuje slalom gigant)
- narciarstwo klasyczne
- saneczkarstwo
- saneczkarstwo
- skeleton (sport powracający do programu IO po 54 latach)
- snowshoeing (sport pokazowy)
Państwa uczestniczące
|
|
Wyniki
Dyscypliny pokazowe
- łyżwiarstwo synchroniczne
- snowshoeing
- pokazy psich zaprzęgów
Hasło
Rozpal w sobie ogień (ang. Light The Fire Within).
Skandale
Podczas Igrzysk Olimpijskich w Salt Lake City ujawniono dwa poważne skandale, pierwszy z nich dotyczył Hiszpana urodzonego w Niemczech Johanna Mühlegga, któremu udowodniono stosowanie dopingu farmakologicznego, ale odebrano mu tylko jeden złoty medal. Drugi skandal dotyczył sędziego, który oszukiwał w konkurencjach łyżwiarstwa figurowego.
Konkurencje
Biathlon
Głównym sportowcem tych igrzysk był norweski mistrz biathlonu Ole Einar Bjørndalen, który zdobył cztery złote medale
Kombinacja norweska
Kombinację zdominował Fin Samppa Lajunen, który zdobył 3 złote medale.
Narciarstwo alpejskie
Chorwatka Janica Kostelić wygrała wszystkie konkurencje w kombinacji, slalomie i w gigancie i była druga w super gigancie. Norweski narciarz Kjetil André Aamodt zdobył 2 złote, 2 srebrne i 2 brązowe medale w kombinacji i super gigancie.
Hokej
W konkurencjach hokejowych nowością było wprowadzenie hokeju kobiet. Wszystkie rywalizacje wygrała drużyna Kanady, zdobywając dwa złote medale.
Skoki narciarskie
Oba konkursy indywidualne wygrał Szwajcar Simon Ammann. Adam Małysz zdobył jeden srebrny i jeden brązowy medal.
Polacy na ZIO
Największym sukcesem Polaków były dwa medale Adama Małysza. Czwarte miejsce zdobyła jeszcze Jagna Marczułajtis w slalomie równoległym snowboardzistek. Był to najlepszy występ Polaków na zimowych igrzyskach między latami 1972, a 2010.
 medal srebrny
medal srebrny
- Adam Małysz – skoki narciarskie – skocznia K-120
 medal brązowy
medal brązowy
- Adam Małysz – skoki narciarskie – skocznia K-90
Klasyfikacja medalowa
| Klasyfikacja medalowa | |||||
| Lp. | Państwo | złoto | srebro | brąz | razem |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 13 | 5 | 7 | 25 | |
| 2 | 12 | 16 | 8 | 36 | |
| 3 | 10 | 13 | 11 | 34 | |
| 4 | 7 | 3 | 7 | 17 | |
| 5 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 13 | |
| 6 | 4 | 5 | 2 | 11 | |
| 7 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 13 | |
| 8 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 7 | |
| 9 | 3 | 5 | 0 | 8 | |
| 10 | 3 | 4 | 10 | 17 | |
Media użyte na tej stronie
Olympic Rings without "rims" (gaps between the rings), As used, eg. in the logos of the 2008 and 2016 Olympics. The colour scheme applied here pertains to the 2016 Olympics in Rio de Janeiro.
Olympic Rings without "rims" (gaps between the rings), As used, eg. in the logos of the 2008 and 2016 Olympics. The colour scheme applied here pertains to the 2016 Olympics in Rio de Janeiro.
Autor: https://phabricator.wikimedia.org/diffusion/GOJU/browse/master/AUTHORS.txt, Licencja: MIT
An icon from the OOjs UI MediaWiki lib.
Autor: https://phabricator.wikimedia.org/diffusion/GOJU/browse/master/AUTHORS.txt, Licencja: MIT
An icon from the OOjs UI MediaWiki lib.
The flag of Navassa Island is simply the United States flag. It does not have a "local" flag or "unofficial" flag; it is an uninhabited island. The version with a profile view was based on Flags of the World and as a fictional design has no status warranting a place on any Wiki. It was made up by a random person with no connection to the island, it has never flown on the island, and it has never received any sort of recognition or validation by any authority. The person quoted on that page has no authority to bestow a flag, "unofficial" or otherwise, on the island.
Łatwo można dodać ramkę naokoło tej grafiki
Official flag used by the Fédération Internationale de Football Association (FIFA) to represent Chinese Taipei in association football matches. Also used at the Olympics from 1986 to 2010.
Łatwo można dodać ramkę naokoło tej grafiki
Flaga Finlandii
Flag of Georgia used from 1990 to 2004, with slightly different proportions than the 1918 to 1921 flag.
Autor: Pedro A. Gracia Fajardo, escudo de Manual de Imagen Institucional de la Administración General del Estado, Licencja: CC0
Flaga Hiszpanii
The Flag of India. The colours are saffron, white and green. The navy blue wheel in the center of the flag has a diameter approximately the width of the white band and is called Ashoka's Dharma Chakra, with 24 spokes (after Ashoka, the Great). Each spoke depicts one hour of the day, portraying the prevalence of righteousness all 24 hours of it.
Flag of Israel. Shows a Magen David (“Shield of David”) between two stripes. The Shield of David is a traditional Jewish symbol. The stripes symbolize a Jewish prayer shawl (tallit).
Flag of Serbia and Montenegro, was adopted on 27 April 1992, as flag of Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (1992-2003).
Flag of Liechtenstein
Flag of New Zealand. Specification: http://www.mch.govt.nz/nzflag/description.html , quoting New Zealand Gazette, 27 June 1902.
The national flag of Kingdom of Thailand since September 2017; there are total of 3 colours:
- Red represents the blood spilt to protect Thailand’s independence and often more simply described as representing the nation.
- White represents the religion of Buddhism, the predominant religion of the nation
- Blue represents the monarchy of the nation, which is recognised as the centre of Thai hearts.
Autor: B1mbo, Licencja: CC BY-SA 2.5
Draw of a silver medal, based in Olympic rings.svg.
- The joining of the rings is not correct drawn.
Autor: B1mbo, Licencja: CC BY-SA 2.5
Drawing of a bronze medal, based on Olympic rings.svg.
Close-up of 2002 Winter Games Olympic Torch
The candidate cities to host the 2002 Winter Olympics, derived from blank world map.
- Green : Applicant cities
- Black: Candidate cities
Flag of Italy from 1946 to 2003, when exact colors were specified.
Flag of Belarus 1995-2012
Olympic flame during 2002 Winter Games in Salt Lake City, Utah, United States.
From the Navy website: Salt Lake City, UT (Feb. 8, 2002) –– Members of the 1980 Gold Medal U.S. Olympic hockey team stand below the Olympic flame at Rice-Eccles Olympic Stadium during the opening ceremonies of the 2002 Winter Olympics in Salt Lake City. The team had the honor of lighting the cauldron to invoke the official start of the competition. U.S. Navy photo by Journalist 1st Class Preston Keres.
Flag of Serbia and Montenegro, was adopted on 27 April 1992, as flag of Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (1992-2003).
Flag of Jamaica. “The sunshine, the land is green, and the people are strong and bold” is the symbolism of the colours of the flag. GOLD represents the natural wealth and beauty of sunlight; GREEN represents hope and agricultural resources; BLACK represents the strength and creativity of the people. The original symbolism, however, was "Hardships there are, but the land is green, and the sun shineth", where BLACK represented the hardships being faced.
Autor: Autor nie został podany w rozpoznawalny automatycznie sposób. Założono, że to Roke~commonswiki (w oparciu o szablon praw autorskich)., Licencja: CC-BY-SA-3.0
2002 winter olympics participants, as listed on w:2002 Winter Olympics (Participating Nations). Host city marked with yellow square (Salt Lake City)